Biotechnology Research and Development
Biotechnology is the use of living organisms, cells, or biological molecules to develop products and processes that enhance human health, agricultural production, and environmental sustainability. At Bioimagene, we combine science and innovation to transform this knowledge into practical applications.

Green Biotechnology: Agriculture and Plants
Green biotechnology focuses on agriculture and plants, including medicinal herbs. Its applications include:
Enhancing crops to increase resistance to diseases and extreme environmental conditions
Producing plants with bioactive compounds for dietary supplements and natural medicines
Promoting sustainable agriculture through environmentally friendly techniques
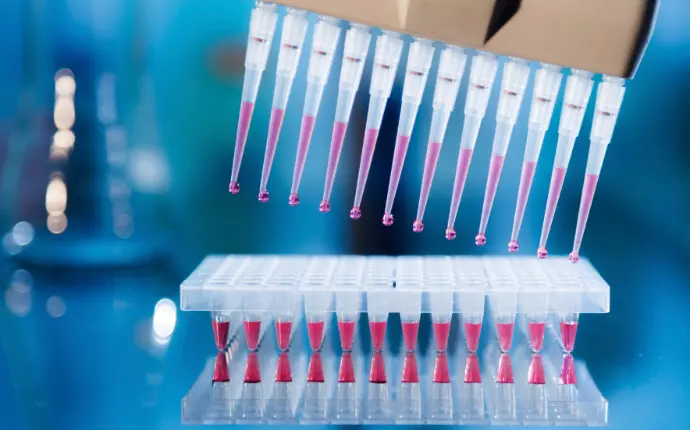
Red Biotechnology: Medicine and Pharmaceuticals
Red biotechnology is related to health and medicine, using techniques such as tissue culture, genetic engineering, and cell and protein research to:
Develop new drugs and vaccines
Create personalized treatments for rare or complex diseases
Study the effects of treatments on cells before clinical application
Blue Biotechnology: Environment and Marine Resources
Blue biotechnology utilizes marine and aquatic resources to:
Develop solutions to protect the environment and eliminate pollutants
Produce bioactive compounds from algae, microorganisms, or marine enzymes
Develop bioproducts and dietary supplements derived from marine resources



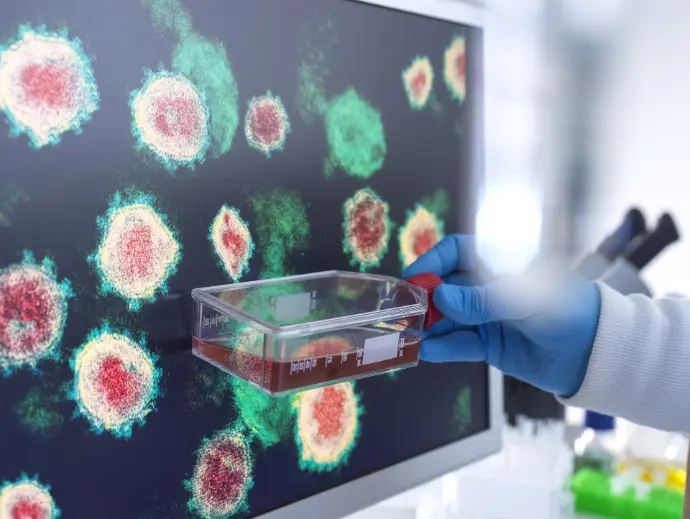



Tissue culture is a technique that allows cells, tissues, or specific organs to grow in a strictly controlled environment, such as temperature, pH, humidity, and nutrients. This technique is crucial for medical research, the development of new drugs, and the production of high-quality cloned plants.
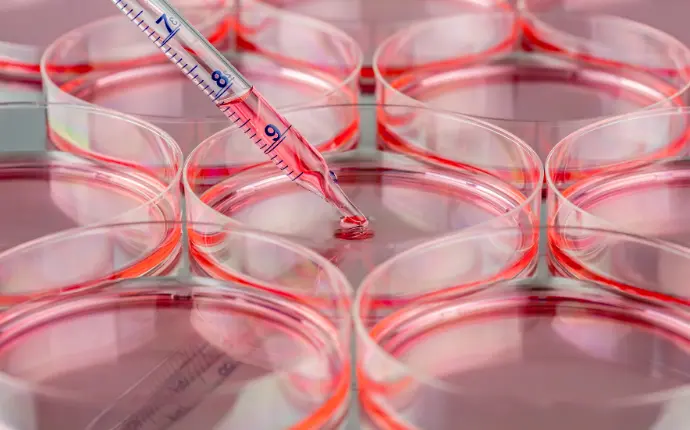
Key Steps of Tissue Culture
Examples of Applications
Medical Applications:
- Culturing cells to test the effects of new drugs
- Studying cancer using laboratory cultured cells
- Creating miniature organ models for diagnosis and personalized treatment
Agricultural Applications:
Producing cloned plants, such as bananas, potatoes, and sugarcane, to increase yield
Preserving rare or endangered plant species
Developing medicinal herbs with consistent quality, such as turmeric and Andrographis paniculata
Diagnostics and Research:
- Testing cell responses to chemicals or treatments
- Using tissue culture as a model to study genetic mechanisms
- Assessing the toxicity of substances before use in humans or animals
Medical biotechnology focuses on using science to prevent, diagnose, and treat diseases.
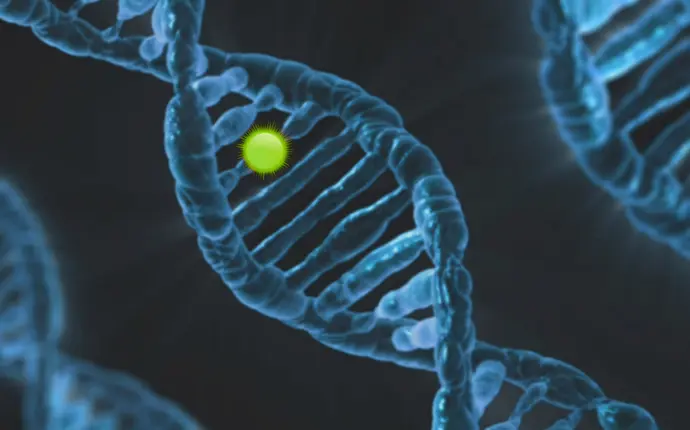


Example::
Synthetic insulin for diabetic patients, monoclonal antibodies for cancer treatment, mRNA vaccines

Technical Procedures:
Identification of biological targets (genes, proteins), gene cloning and expression in model organisms, preclinical testing, and clinical trials.

Diagnostic Tools:
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), molecular imaging, PCR testing for rapid pathogen detection.
Traditional Thai herbal formulas are considered an important source of bioactive compounds.
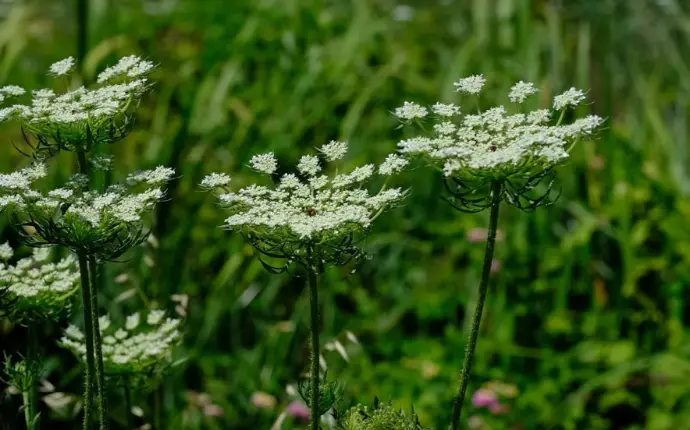

Example:
- Andrographis paniculata: antiviral and anti-inflammatory
- Curcuma longa (turmeric): antioxidant and anticancer
- Centella asiatica: wound healing and brain health
Biological Applications:
Extraction of active compounds, separation and purification using chromatography, testing both in vitro and in vivo.
Diagnostics:
Molecular screening to identify new bioactive compounds.
Agricultural biotechnology helps enhance food security and sustainability.
Example:
- Golden Rice enriched with vitamin A
- Bt cotton resistant to insects
- Long shelf-life tomatoes
Technical Procedures:
Selection using molecular markers (MAS), gene transfer via Agrobacterium, gene editing with CRISPR-Cas9.
Diagnostics:
Detection of plant pathogens using ELISA or PCR, and the use of biosensors to monitor soil quality.
This helps reduce the use of agrochemicals, improve nutrition, and adapt to changing climate conditions.

Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
Genetically modified organisms have been engineered to enhance specific beneficial traits.
Example:
- Herbicide-tolerant corn
- Soybeans with health-beneficial fatty acids
- Genetically modified mosquitoes to reduce the spread of dengue fever
Process:
Identify the target gene → insert into a vector → introduce into the organism → select and verify the results.
Diagnostics:
Verification using PCR or genetic sequencing for food safety.
Despite controversies, GMOs are considered an important tool to address food shortages and mosquito-borne diseases.

Medical Applications:
- Prenatal genetic testing
- Cancer diagnosis using genetic information
- Identification of genes associated with rare diseases

Agricultural Applications:
Breeding plants and animals to be disease-resistant

Tools:
DNA sequencing, microarray, quantitative PCR

01

Example:
Production of human insulin in E. coli, creation of growth hormones, development of drought-resistant plants
02

Steps:
Gene isolation → Cloning → Inserting into host cells → Culturing and expression → Purifying the protein
03

Diagnosis:
Development of molecular probes and biomarkers to monitor treatment
Our latest content
Check out what's new in our company !





